Damage Identification of Metal-Composite Bonded Joints using Electromechanical Impedance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.137.1.147159Keywords:
structural health monitoring, electromechanical impedance, finite element analysis, adhesive bonding, metal-compositeAbstract
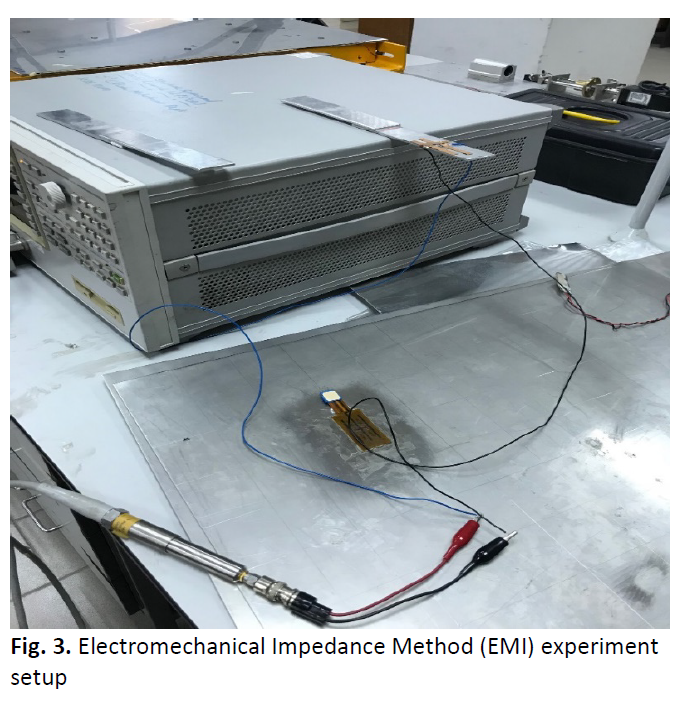
In critical applications such as the aerospace, marine and automotive industries, it is very important to maintain the safety of every component of the structures and also to monitor their conditions periodically. Since the use of composite has been more widely utilized to promote a better strength-to-weight ratio, it is especially crucial to foresee a combination of metal and composite in a single structure. However, the adhesively bonded joint is very unpredictable and it is remarkably difficult to estimate its failure. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to perform Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) to identify if damage appears at the joint. Traditional non-destructive approaches are less accurate; vibration causes a change in the stiffness of the sensor causing a false alarm. The EMI method is used in which the dynamic properties of metal-composite bonded joints are examined to identify damage in the structure. A defect that modifies the structure’s physical properties, for instance, its stiffness and damping will cause the real part of the impedance response to be shifted to lower frequencies when the electromechanical impedance (EMI) method is performed on Metal-to-metal single lap joint, Metal to thick composite single lap joint, Metal to thin composite single lap joint. The damage quantifying metric Correlation Coefficient Deviation Metric (CCDM) of value 1.1386 and Root Mean square Deviation (RMSD) value of 0.7281 indicates the highest damage depth in the case of Metal to thick composite single lap joint.





 "SHARE YOU KNOWLEDGE FOR A BETTER TOMORROW"
"SHARE YOU KNOWLEDGE FOR A BETTER TOMORROW"