Driver Drowsiness Detection using Transfer Learning and Computer Vision
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.137.1.176190Keywords:
drowsiness detection, eye state, computer vision, transfer learning, convolution neural networksAbstract
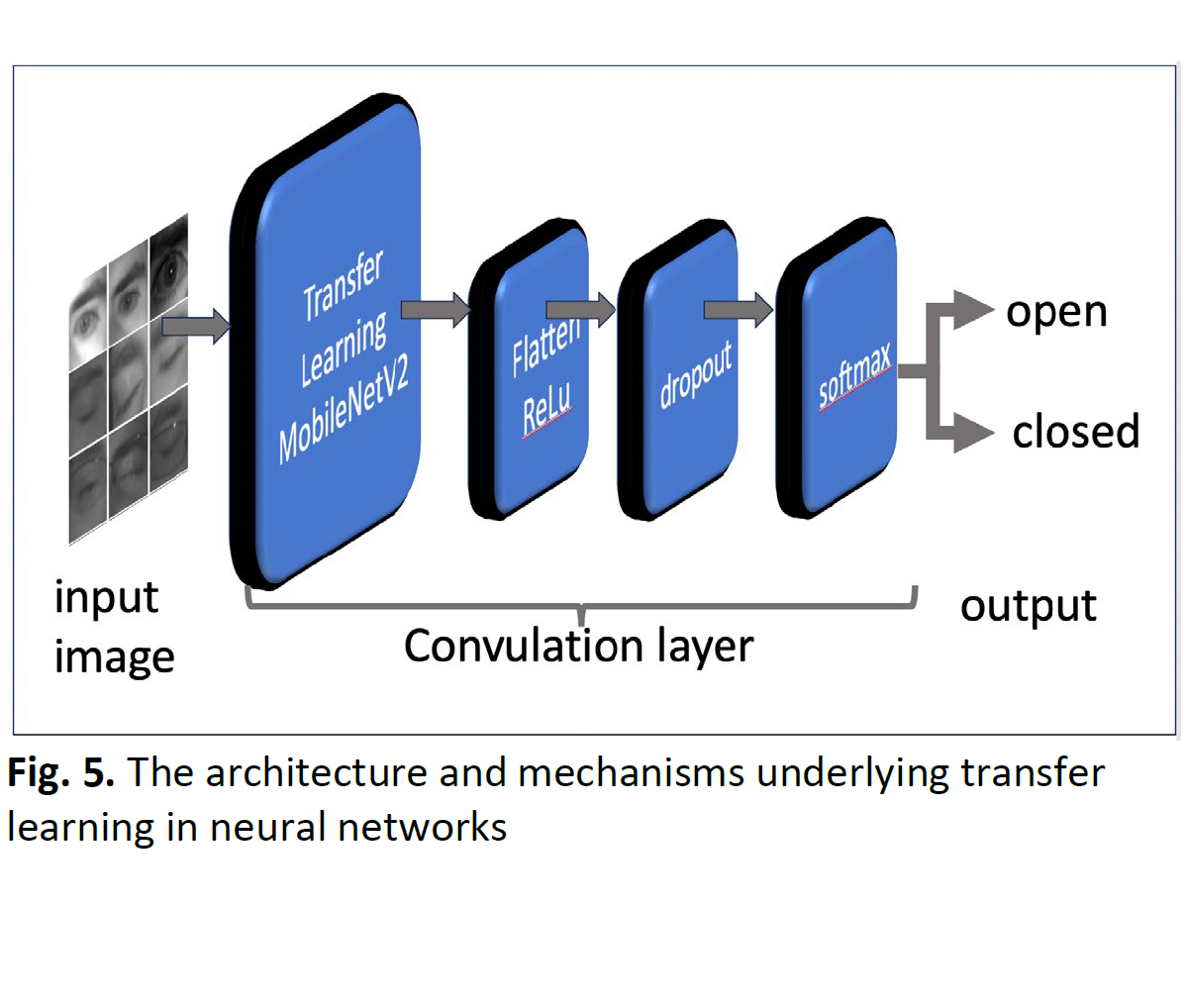
Driver drowsiness is a common causes of road accidents resulting in injuries, fatalities, property damage and crash severity, especially for vulnerable road users. This issue requires the development of an effective drowsiness detection and alert system. Web cameras provide a low-cost, real-time solution for monitoring driver alertness. However, accurately classifying eye states as open or closed is challenging, particularly when drivers wear glasses or encounter varying lighting conditions. This study proposes a method using transfer learning and computer vision to detect driver drowsiness. The method uses computer vision to identify the eye state of a driver. A dataset from the MRL Eye Dataset will be used to train the system. The webcam will be placed closely in front of the user to detect the eyes of the driver. The system is designed to deal with face areas in the video captured. The videos are converted into image frames per second to locate the eye location. When the eyes are located, the eye state will determine whether the eyes are open or closed. If the eyes are detected to be closed for more than 10 consecutive frames, the eyes are considered closed and this shows that the driver is drowsy, at which point the driver will get alerted. This system able to detect the driver's drowsiness with or without the presence of eyeglasses in both ideal and poor lighting conditions. The experimental results of this system have an accuracy of 97% and low computational complexity. Overall, this study presents a significant contribution to the field of drowsiness detection by proposing a real-time, low-cost and accurate system that can be installed in vehicles to ensure safe transportation Drowsiness.





 "SHARE YOU KNOWLEDGE FOR A BETTER TOMORROW"
"SHARE YOU KNOWLEDGE FOR A BETTER TOMORROW"