Thermal Stability Analysis of Az91-Cnt Magnesium Nanocomposites Under Controlled Thermal Exposure
Keywords:
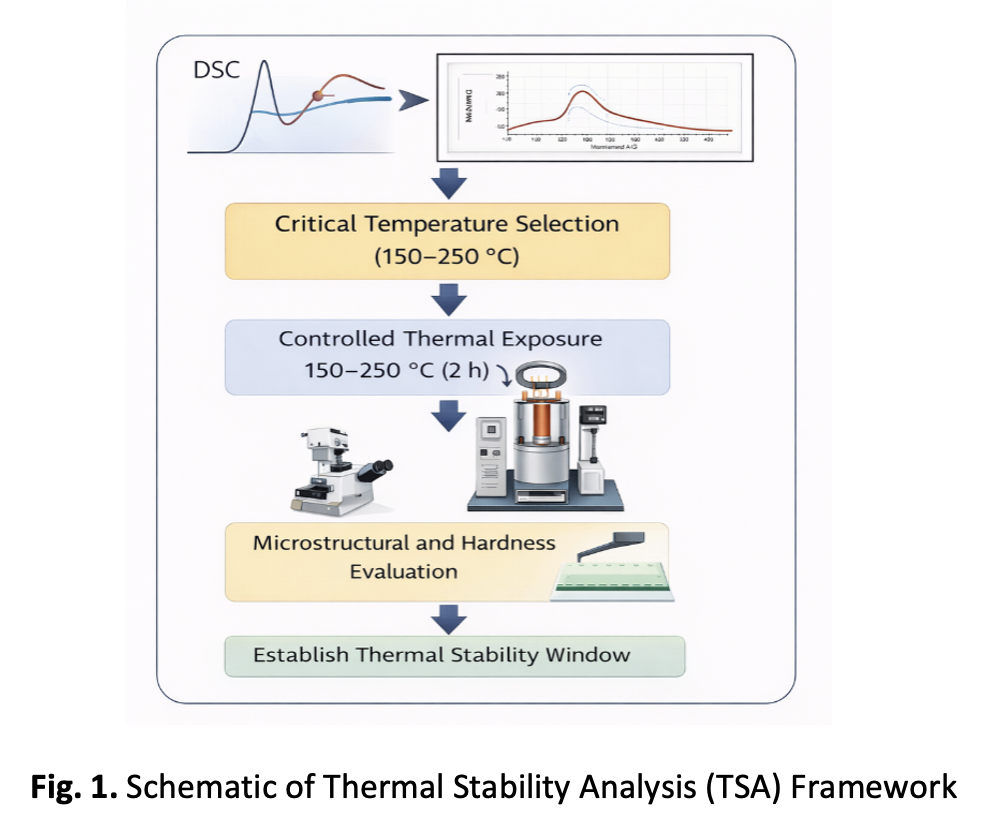
Thermal stability analysis, AZ91 magnesium alloy, carbon nanotubes, thermal exposure, phase stabilityAbstract
Thermal stability is a critical requirement for magnesium-based materials intended for applications involving prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. However, conventional thermal characterisation methods mainly focus on identifying phase transformation temperatures and provide limited information on time-dependent microstructural and mechanical stability under service-like conditions. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the thermal stability of AZ91 magnesium alloy reinforced with carbon nanotubes through a stability-oriented assessment framework. A comprehensive Thermal Stability Analysis was employed to investigate the behaviour of AZ91–CNT magnesium nanocomposites subjected to controlled thermal exposure. Based on critical thermal events identified from thermal analysis, both reinforced and unreinforced samples were exposed to selected isothermal temperatures, followed by systematic evaluation of microstructural evolution and hardness retention. The results demonstrate that carbon nanotube reinforcement significantly enhances the thermal stability of AZ91 magnesium alloy by delaying the dissolution and coarsening of the β-Mg₁₇Al₁₂ intermetallic phase. The AZ91-CNT nanocomposites exhibited minimal hardness degradation and preserved microstructural features when exposed to temperatures within the range of 150-200 °C, whereas the unreinforced AZ91 alloy showed earlier onset of thermal softening and microstructural instability. The findings reveal a clear extension of the stable operating temperature window for the CNT-reinforced alloy compared to the unreinforced counterpart. This enhanced thermal stability is attributed to the role of carbon nanotubes as diffusion barriers and microstructural pinning sites that restrict phase instability during prolonged thermal exposure. In conclusion, the Thermal Stability Analysis approach provides a practical and service-relevant evaluation of material performance and establishes reliable thermal operating limits for AZ91-CNT magnesium nanocomposites intended for temperature-sensitive engineering applications.